Difference between CDM and CDM messages
Let us wrap up our discussion on microlearnings related to the Canonical Data Model (CDM) by clarifying the distinction between the CDM itself and CDM messages. In this microlearning, we will explore how the CDM encompasses all relevant entities and attributes across your integration landscape, while CDM messages are designed for specific data types, containing only the entities and attributes pertinent to each data piece.
If you have any questions along the way, feel free to reach out to us at academy@emagiz.com.
1. Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of the eMagiz platform
2. Key concepts
This microlearning centers around understanding the difference between CDM and CDM messages.
- With CDM we mean: The Canonical Data Model that plays a vital and central role while exchanging data between various systems via the messaging pattern.
- A complete CDM consists of the collection of entities that are used or going to be used in the various CDM messages.
3. Difference between CDM and CDM messages
Simply put the difference between the CDM and the CDM messages is as follows:
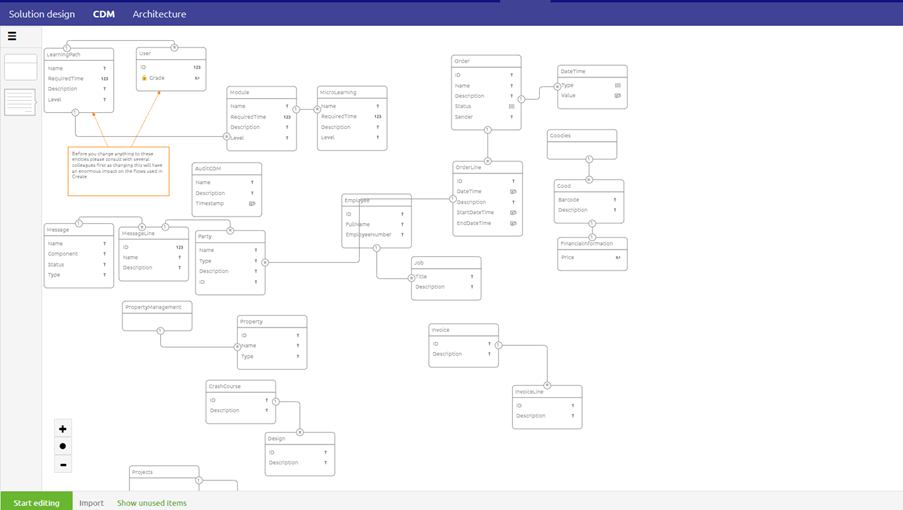
- The CDM holds all entities and attributes that are relevant within the context of your complete integration landscape.
- The CDM message is tailor-made for a specific piece of data (i.e. Order, Invoice, Employee) and only holds the entities and attributes relevant for that piece of data.
When a new system message needs to be processed, new entities have to be created. These entities have to be generic, according to the language and notation of the CDM. Thus, the entities have to be created in the CDM first. After that, these entities can be created in a CDM message, gateway message, or topic message. Once the entities and attributes have been created in a CDM message, gateway message, or topic message, they can be mapped to the entities and attributes from the system message.
Note that both the CDM and CDM/gateway/topic message show all entities and attributes that are relevant within the context of your complete integration landscape. The main difference is that the CDM message only holds the entities and attributes that are tailor-made for a specific piece of data. This is indicated in green.
Below, the CDM for a model is shown.
An example of a CDM message for this model is the following:
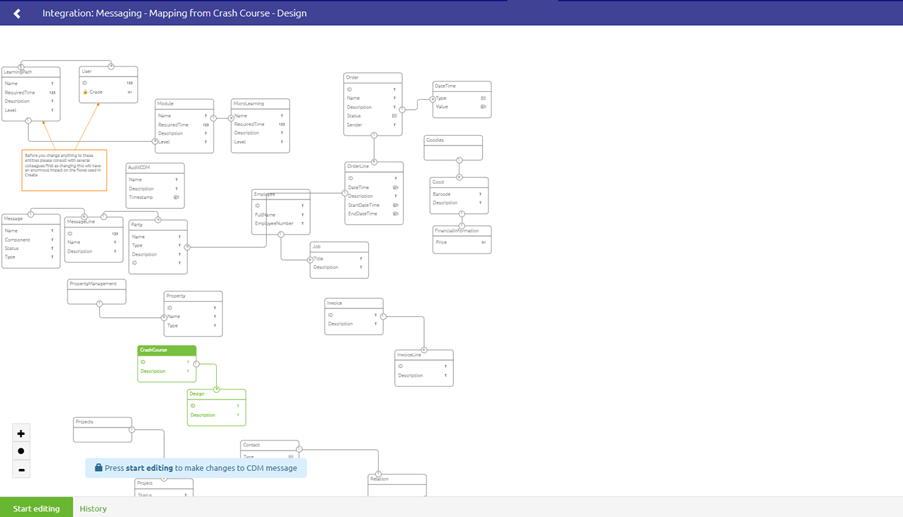
This CDM message holds the entities CrashCourse and Design, as indicated in green.
Once the entities and attributes have been created, the message definitions have to be added. As explained before, a system message is specific to the system, whereas a CDM/gateway/topic message is generic and consistent across systems. For the system message, it is possible to add complete entities, but it is also possible to add only one attribute to the system message definition. This can be done by using the Toggle canvas edit mode button, hovering over the desired attribute and clicking on it. The attributes can also be removed individually.
For a CDM/gateway/topic message it also possible to add and remove entities and attributes. This can be done by hovering over the desired entities or attributes and clicking on them. The Toggle canvas edit mode button is not present here, it is only needed to hover over the entities/attributes. A minus will appear when the entity/attribute is already present in the message definition. By clicking, the entity/attribute will then be removed from the message definition. In case a plus appears, the entity/attribute is not yet present in the message definition, and can be added by clicking on it.
4. Key takeaways
- CDM: Represents the complete collection of entities and attributes relevant to your entire integration landscape, providing a comprehensive view of all data elements used across systems.
- CDM Messages: Tailored for specific data types (e.g., Order, Invoice, Employee), these messages contain only the entities and attributes relevant to that particular data, ensuring targeted data handling.
5. Suggested Additional Readings
If you are interested in this topic and want more information on it please read the help text provided by eMagiz and read the following link:
